Lubrication Effectiveness: Operating temperatures significantly impact the viscosity and thermal stability of lubricants used in screw compressor bearings. High temperatures can cause lubricants to degrade or oxidize faster, reducing their ability to form a protective film between bearing surfaces. This breakdown leads to increased friction, heat generation, and wear. Conversely, at lower temperatures, lubricants may thicken, reducing their flowability and effectiveness in maintaining proper lubrication across bearing components. Maintaining the correct operating temperature helps ensure that lubricants perform optimally, extending the life of bearings and reducing maintenance costs.
Bearing Material Properties: Bearings in screw compressors are typically made from materials designed to withstand specific temperature ranges. High temperatures can exceed the material's thermal limits, causing bearings to lose their hardness and dimensional stability. This thermal expansion can lead to increased clearance between bearing components, which in turn can result in greater friction and wear. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can induce metallurgical changes such as softening or even thermal cracking in bearing materials, compromising their structural integrity and lifespan.
Clearance Changes: Temperature fluctuations directly affect the dimensional stability of bearings. As temperatures rise, materials expand, potentially reducing the clearance between bearing components. This reduction in clearance can lead to increased contact pressure and frictional heat generation within the bearing, accelerating wear. Conversely, at lower temperatures, bearings may contract, altering their operating characteristics and potentially causing issues such as inadequate lubricant flow or insufficient load support. Properly managing operating temperatures helps maintain consistent bearing clearances and ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Fatigue and Wear: Elevated operating temperatures accelerate wear mechanisms within screw compressor bearings. Thermal energy increases the rate of material fatigue and surface degradation, leading to phenomena such as abrasive wear, adhesive wear, and surface scoring. High temperatures also promote chemical reactions within lubricants and bearing materials, further exacerbating wear processes. Over time, these wear mechanisms can compromise bearing integrity, leading to increased friction, reduced efficiency, and ultimately, premature failure. Monitoring and controlling operating temperatures are essential for mitigating wear-related issues and maximizing bearing service life.
Seal Performance: Temperature extremes can adversely affect the performance of seals and gaskets used in screw compressor bearings. High temperatures can cause seals to harden, lose elasticity, or degrade prematurely, compromising their ability to maintain proper lubrication and exclude contaminants. This degradation can lead to increased friction, accelerated wear, and potential oil leakage from the bearing assembly. Conversely, at lower temperatures, seals may become less flexible, increasing the risk of seal failure and subsequent bearing damage. Ensuring effective sealing performance through proper material selection and regular inspection is critical for preserving bearing integrity and minimizing operational disruptions.
Cooling System Efficiency: Efficient cooling systems are essential for managing operating temperatures within screw compressors. Inadequate cooling, such as insufficient airflow or malfunctioning cooling components, can result in overheating of bearings. Excessive heat not only accelerates wear processes but also compromises the thermal stability of lubricants and bearing materials. This can lead to increased energy consumption, reduced compressor efficiency, and higher maintenance costs. Implementing robust cooling strategies, including regular maintenance of cooling components and monitoring of temperature trends, helps ensure optimal operating conditions for screw compressor bearings.
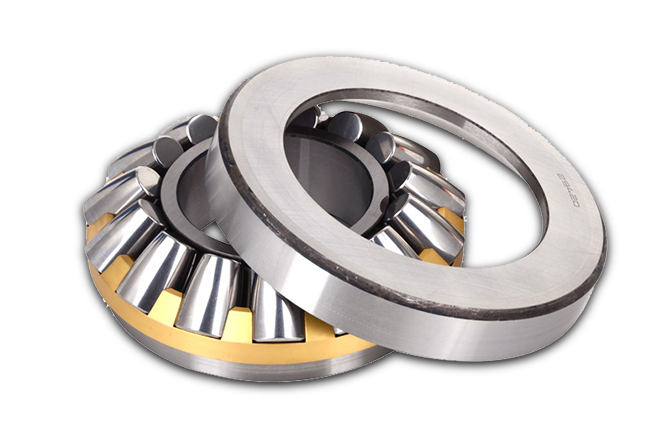
Screw Compressor Thrust Spherical Roller Bearings


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch























