The selection of bearing clearance in a gearbox is a critical factor that directly impacts the performance and lifespan of the bearings. The operating conditions, including load and speed, play a significant role in determining the appropriate bearing clearance. Here's how these factors influence the selection:
Load:
Heavy Load: When dealing with heavy loads, such as those common in industrial gearbox applications, it is essential to choose bearings with larger clearances. Heavy loads result in greater forces acting on the bearings, and larger clearances allow for more significant deformations without causing excessive stress. This is crucial for preventing premature wear and ensuring the longevity of the bearings under sustained heavy loads.
Light Load: In situations where the load is comparatively lighter, bearings with smaller clearances can be considered. This approach provides more precise control over internal clearances, contributing to increased precision and responsiveness in the gearbox.
Speed:
High Speed: High-speed gearboxes generate substantial heat due to increased friction. Opting for larger clearances becomes imperative in this scenario. Larger clearances accommodate the thermal expansion that occurs at higher speeds, reducing the risk of thermal-related failures and ensuring stable performance during rapid operation.
Low Speed: Lower-speed applications offer the flexibility to use bearings with smaller clearances. This choice enhances the stiffness of the bearing system, maintaining load-carrying capacity without compromising on lubrication effectiveness, which is crucial for slower operational speeds.
Temperature:
Elevated Temperatures: Operating at elevated temperatures, often associated with higher speeds or heavier loads, demands careful consideration of larger clearances. This choice is essential for managing thermal expansion effectively, preventing overheating, and extending the life of the bearings in challenging thermal conditions.
Moderate Temperatures: Applications with moderate temperatures allow for a balanced approach to clearances. This involves ensuring proper thermal expansion while maintaining the bearings' ability to carry loads effectively, contributing to overall system efficiency and reliability.
Lubrication:
Insufficient Lubrication: In cases of poor lubrication, larger clearances become a critical factor. Larger clearances compensate for potential variations in the lubricating film thickness, reducing the risk of direct metal-to-metal contact and mitigating friction-related issues that may arise from inadequate lubrication.
Effective Lubrication: When effective lubrication practices are in place, smaller clearances can be considered. This promotes optimal load distribution, minimizing the risk of friction-related problems and ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of the bearing system.
Application Specifics:
Shock Loads: Gearbox applications subjected to frequent shock loads require bearings with larger clearances. This design choice allows the bearings to absorb impact energy, reducing the risk of damage and ensuring a longer lifespan under challenging operating conditions.
Continuous Operation: For applications requiring continuous operation, a nuanced approach to clearances is essential. This involves considering factors such as thermal management, load distribution, and system stability to provide consistent and reliable performance over extended periods.
Material Selection:
Material Properties: The properties of the chosen bearing material significantly influence clearance selection. Different materials exhibit distinct thermal expansion characteristics, demanding a tailored approach to clearances for optimal performance and longevity in the specific application. It's crucial to select materials that can withstand the operating conditions and align with the desired clearance strategy.
NNC-Double Row Full Complement Cylindrical Roller Bearings
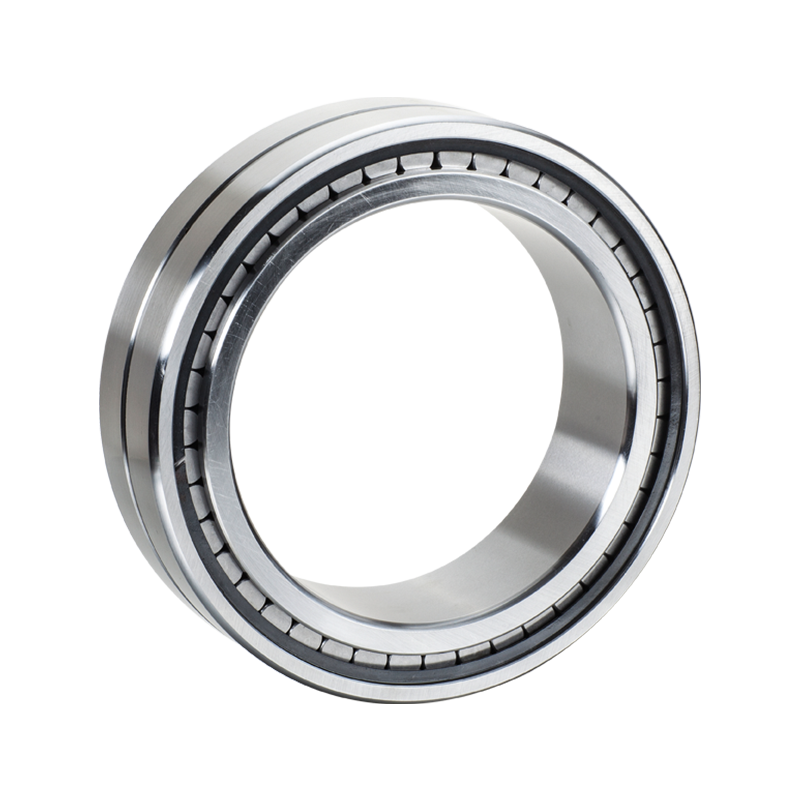

NNC-Double Row Full Complement Cylindrical Roller Bearings


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch