Bearing lubrication plays a crucial role in the performance and lifespan of motor bearings. Proper lubrication helps to reduce friction, dissipate heat, prevent wear, and protect against corrosion. Here's how bearing lubrication impacts these aspects:
1.Friction Reduction:
Bearing lubrication creates a thin film of lubricant between the rolling elements (balls or rollers) and the raceways (inner and outer rings) of the bearing. This film separates the surfaces, reducing direct metal-to-metal contact. By minimizing friction, the lubricant enables smoother rotation of the bearing components. This reduction in friction helps to conserve energy and allows the motor to operate more efficiently, translating into lower energy consumption and reduced wear on the bearing surfaces.
2.Heat Dissipation:
As the motor operates, friction between the rolling elements and the raceways generates heat. Without proper lubrication, this heat can accumulate and lead to localized overheating. Adequate lubrication dissipates the heat, distributing it across a larger surface area. This prevents excessive temperature rises that could cause thermal expansion, degradation of lubricants, and potential damage to the bearing components.
3.Wear Prevention:
Lubricants act as protective barriers between the bearing components. The lubricating film prevents direct metal-to-metal contact, reducing the wear on the rolling elements and raceways. This wear reduction is particularly important in high-load and high-speed applications, where increased friction and wear could otherwise lead to premature bearing failure.
4.Corrosion Protection:
Bearings in industrial or outdoor environments are exposed to moisture, chemicals, and contaminants that can cause corrosion. Lubricants create a barrier that shields the bearing surfaces from these elements, preventing rust and corrosion. This protection is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the bearing and preventing premature failure.
5.Sealing and Contaminant Exclusion:
Some lubricants possess sealing properties that help to keep contaminants out of the bearing assembly. These contaminants, such as dust, dirt, and particles, can infiltrate the bearing and lead to abrasive wear, increased friction, and compromised performance. Lubricants with effective sealing capabilities extend the bearing's life by maintaining a clean operating environment.
6.Noise and Vibration Reduction:
Well-lubricated bearings experience reduced levels of vibration and noise. Lubricants absorb and dampen vibrations that can arise from the interactions between rolling elements and raceways. This vibration reduction contributes to smoother motor operation and a quieter working environment.
7.Prevention of Fretting and Micro-Pitting:
Fretting, caused by slight movements between stationary and moving parts, can lead to surface damage and accelerated wear. Lubrication prevents fretting by providing a cushioning effect that absorbs these small oscillations. Additionally, lubricants guard against micro-pitting, a form of surface fatigue that can cause small, localized craters on bearing surfaces and ultimately compromise the bearing's integrity.
8.Load Distribution:
Lubrication helps distribute loads more evenly across the bearing's contact surfaces. This even distribution minimizes the risk of stress concentrations forming in localized areas. In turn, this promotes a longer lifespan for the bearing by preventing premature fatigue failure due to uneven loading.
9.High-Speed Performance:
In high-speed applications, the role of lubrication becomes critical. Lubrication reduces friction and heat generation, enabling the bearing to withstand the demands of rapid rotation. Proper lubrication ensures that the bearing components glide smoothly rather than skid or slide, preventing wear and damage that can occur due to extreme speeds.
To ensure the best performance and longevity of motor bearings through lubrication:
Choose the right lubricant based on factors like speed, load, temperature, and environmental conditions.
Monitor and maintain the appropriate lubrication level to prevent over-lubrication or under-lubrication.
Consider using sealed or shielded bearings that come pre-lubricated and are designed to retain lubrication while keeping contaminants out.
Regularly inspect bearings for signs of wear, overheating, or contamination, and replenish or replace lubricant as needed.
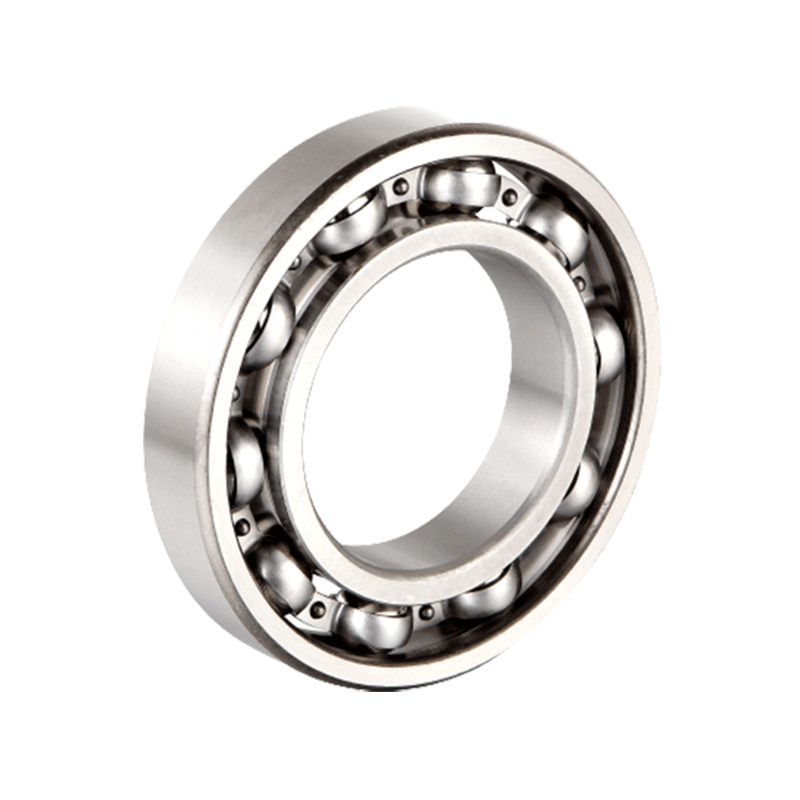


Single row deep groove ball bearings are characterized by their simple yet effective design, consisting of an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of balls, and a cage to keep the balls separated and evenly spaced. This design allows for reduced friction and enhanced load distribution, resulting in improved efficiency and durability.

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch























