Several factors can contribute to bearing failure in automotive systems. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring the reliability and longevity of bearings in vehicles. Some of the main factors include:
1.Improper Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and dissipating heat within bearings. Inadequate lubrication, incorrect lubricant selection, or contaminated lubricants can compromise the lubricating film between rolling elements and raceways. This leads to increased friction, wear, and eventually, bearing failure. Regular analysis of lubricants and adherence to manufacturer specifications are crucial to prevent this issue.
2.Contamination:
Contaminants like dust, dirt, water, and metal particles compromise the integrity of bearings. These particles infiltrate the bearing assembly, leading to abrasion, scoring, and surface fatigue. Effective sealing systems and proper maintenance practices, including keeping the environment clean during assembly, are vital in preventing contamination-related failures.
3.Misalignment:
Misalignment causes uneven loading on the bearing, leading to stress concentrations. This stress can result in localized wear, brinelling (indentations on bearing surfaces), and reduced fatigue life. Precision alignment during installation and the use of self-aligning bearings in applications prone to misalignment can mitigate this problem.
4.Overloading:
Excessive loads strain bearings beyond their rated capacity, causing plastic deformation, loss of clearance, and increased operating temperatures. Careful consideration of load ratings, dynamic and static, as well as operating conditions, ensures bearings are selected appropriately for the application, preventing overload-related failures.
5.Poor Installation:
Incorrect installation practices, such as improper fits, forceful assembly methods, or inadequate securing of components, can induce stress and misalignment in the bearing. This can be mitigated through training and adherence to installation procedures outlined by the bearing manufacturer, ensuring precise fits and alignments.
6.Corrosion:
Corrosion weakens bearing surfaces, leading to pitting and spalling. It often occurs due to exposure to moisture, corrosive chemicals, or improper storage conditions. Proper sealing, material selection (such as stainless steel), and the use of corrosion-resistant coatings are effective measures to combat corrosion-related failures.
7.Fatigue:
Bearings subjected to cyclic loading experience metal fatigue over time. This repetitive stress can lead to cracks, raceway spalling, and eventual failure. Fatigue-resistant materials, proper lubrication, and periodic inspections are essential to monitor fatigue-related wear and replace bearings before failure occurs.
8.High Temperatures:
Excessive heat disrupts the microstructure of bearing materials, reducing hardness and leading to accelerated wear. Efficient cooling systems, suitable lubricants with high-temperature stability, and heat dissipation mechanisms are critical in preventing temperature-induced failures.
9.Vibration:
Excessive vibration imposes additional stress on bearings, accelerating wear and fatigue. Vibration analysis and damping techniques help identify problematic frequencies and minimize vibrations, ensuring longer bearing life.
10.Poor Maintenance:
Regular inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn-out bearings are fundamental to prevent unexpected failures. Predictive maintenance techniques, such as vibration analysis and thermal monitoring, aid in identifying potential issues before they escalate.
11.Inadequate Sealing:
Damaged or ineffective seals allow contaminants to infiltrate the bearing, causing abrasive wear and lubricant contamination. High-quality seals, proper installation, and periodic inspection of sealing systems are essential to prevent ingress of harmful particles.\
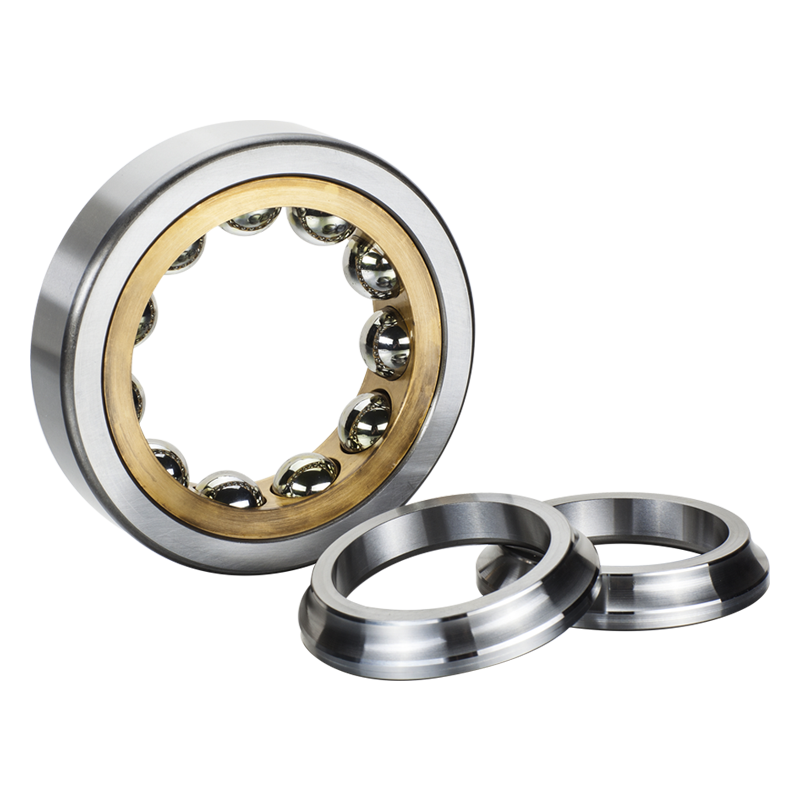


To allow the bearings to accept the maximum number of balls, four point contact ball bearings are designed with split inner ring or with split outer ring so these bearings have two basic types, one is featured two half inner ring (QJ series), an other is featured two half outer ring (Q series).

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch























