Ensuring proper alignment of shafts and housings is crucial for optimizing the performance and longevity of four-point contact ball bearings. Here are the steps that should be taken:
Use precision alignment tools: Invest in cutting-edge alignment equipment characterized by exceptional precision and accuracy. Select from a range of advanced tools including dial indicators, laser alignment systems, or alignment telescopes, each offering distinct advantages in measuring and adjusting alignment parameters. These tools provide precise readings essential for achieving alignment conditions.
Check initial alignment: Prior to initiating bearing installation, conduct a meticulous examination of the initial alignment status of shafts and housings. Employ sophisticated measurement techniques to assess alignment parameters such as angularity, parallelism, and concentricity. Utilize recommended tolerances as benchmarks, ensuring that deviations are promptly identified and rectified to establish a solid foundation for bearing installation.
Inspect mounting surfaces: Execute a comprehensive inspection of the mounting surfaces on both shafts and housings with meticulous attention to detail. Employ advanced inspection techniques such as surface profilometry or digital microscopy to identify surface irregularities, defects, or damage that may compromise alignment integrity. Employ corrective measures such as machining, grinding, or surface treatment to rectify any identified issues prior to bearing installation.
Properly mount bearings: Execute the bearing mounting process with meticulous precision, adhering strictly to recommended procedures and practices. Utilize specialized mounting equipment and fixtures designed to facilitate accurate alignment and minimize handling-induced errors. Employ precision measurement tools to verify alignment parameters during the mounting process, ensuring that bearings are seated securely and aligned precisely with the shafts and housings.
Use appropriate mounting methods: Select mounting methods and techniques tailored to the specific characteristics of the bearings and the operational requirements of the application. Evaluate factors such as bearing size, material, and configuration, as well as environmental conditions and operational constraints, to determine the suitable mounting approach. Consider advanced mounting techniques such as thermal induction heating, hydraulic mounting, or precision press fitting to achieve alignment without inducing mechanical stress or distortion.
Check for parallelism: Validate the parallelism between shafts and housings along their entire length using metrology tools and techniques. Employ precision laser alignment systems or optical alignment instruments to assess parallelism accurately, taking into account factors such as shaft deflection, thermal expansion, and structural misalignment. Implement corrective measures such as shimming, repositioning, or realignment to achieve parallel alignment within specified tolerances.
Adjust as necessary: Continuously monitor alignment parameters during bearing installation and operation, utilizing real-time feedback from advanced alignment systems to identify deviations promptly. Employ sophisticated adjustment mechanisms such as precision actuators, hydraulic jacks, or motorized positioning systems to execute micro-adjustments and fine-tune alignment parameters as needed. Implement iterative alignment procedures to optimize alignment accuracy and minimize dynamic misalignment effects during operation.
Consider thermal expansion: Incorporate thermal compensation strategies into the alignment process to mitigate the effects of temperature variations on shafts and housings. Utilize advanced thermal modeling techniques to predict thermal expansion behavior under varying operating conditions, enabling proactive adjustment of alignment parameters to maintain alignment integrity. Employ materials with low coefficients of thermal expansion or incorporate thermal isolation techniques to minimize the impact of temperature fluctuations on alignment stability.
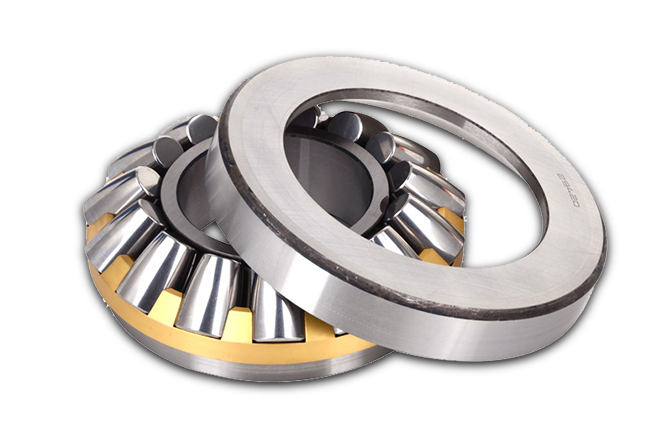
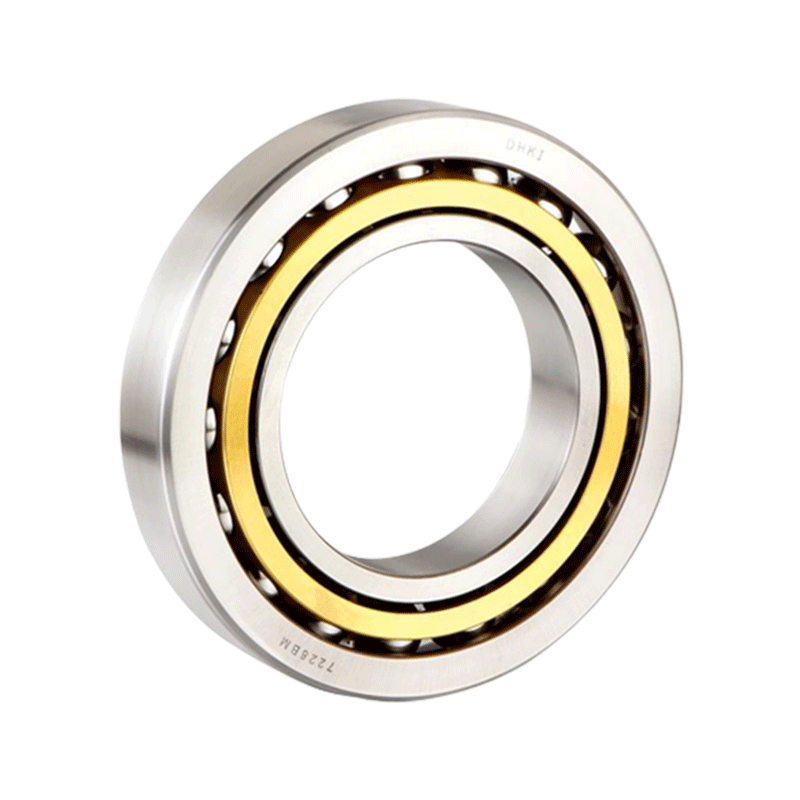
Four Point Contact Ball Bearings


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch























